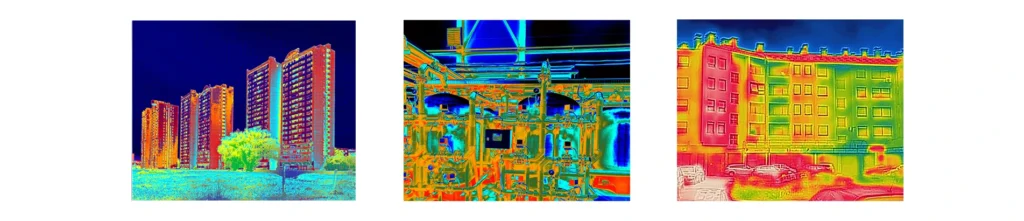
What is thermography?
It is a technology that makes infrared radiation visible. It allows by means of a camera or another device such as a drone equipped with an infrared camera to determine the condition of an object by examining its surface (e.g.: roof, building facade, electrical panel etc…). Thermography makes the invisible visible unlike a visual inspection.
The thermal camera: good or bad for the specific inspection sought?
There are several thermal imaging cameras available on the market and it is not always easy to choose the one that will meet the requirements of the thermal application. Certain parameters must be considered when choosing a thermal imaging camera such as resolution (measured in pixels), distance from the object to be thermographed and the temperature scale required for the thermographic measurement. There is no single thermal imaging camera that will be the ultimate solution for all thermography applications.
Examples of common errors with non-certified thermography inspectors include.
⮚ Using the wrong camera for the thermography job at hand: example: using a low resolution thermal camera for small objects to be thermographed.
⮚ Wrong thermographic interpretation: example: forgetting to enter the reflected temperature prevents the thermographer from correctly interpreting the thermal images.
Applications: thermography can be used for residential and commercial inspection to detect wet or missing insulation, heat loss, roof infiltration or water damage etc…. There are many other applications for thermography. It is important to understand that each thermographic application requires the use of specific protocols. That is, a method of applying specific procedures to perform thermography. For example, to perform a thermographic roof inspection, it must be done two hours after sunset to obtain a thermal inversion, which allows the detection of roof water damage invisible to the naked eye. Most applications for modern thermography are qualitative. This method of comparative thermography is based on temperature differences rather than actual temperatures. It is also important to know what thermography can and cannot do.
What thermography can do:
⮚ Can detect wet insulation
⮚ Heat loss (air infiltration or exfiltration)
⮚ Leaking roof: water damage invisible to the naked eye
⮚ Gas loss in high-performance windows (argon)
⮚ The presence of insects (wasp nest)
⮚ The presence of animal nests (squirrel nests)
⮚ Electrical hazards that are invisible to the naked eye
⮚ The poor quality of building construction
⮚ Could detect the source of the water leak & water infiltration
⮚ Could detect the presence of mold!
When a thermographer buys a thermal camera, they don’t necessarily know the breadth of knowledge required to interpret the captured information. Understanding the camera menus and using the basic functions is easy to learn but it is the proper interpretation of the images that is important. Thermal cameras are excellent tools when you know how to use them properly and interpret the images correctly.